Methane gas and its importance in climate change
|
Methane (CH4) is a potent greenhouse gas that is second only to carbon dioxide (CO2) in terms of emissions caused by human activities. It has a global warming potential approximately 25 times greater than CO2 over a 100-year period. So, despite its relatively short atmospheric lifetime of about 12 years, methane’s impact on climate change is profound and immediate. Sources and Impact of Methane EmissionsMethane emissions arise from both natural and anthropogenic sources. Natural sources include wetlands, oceans, and methane hydrates, while human activities such as agriculture (particularly livestock enteric fermentation and rice paddies), fossil fuel extraction, and waste management (landfills and wastewater treatment) are significant contributors. According to the Global Methane Budget, human activities contribute approximately 60% of global methane emissions, amounting to around 580 million metric tons annually. Addressing methane emissions is critical for mitigating climate change, especially in the short term: reducing methane emissions can swiftly lower atmospheric concentrations, providing immediate climate benefits. For instance, a 45% reduction in methane emissions by 2030 could prevent 0.3°C of global warming by 2045, according to the United Nations Environment Programme (UNEP).
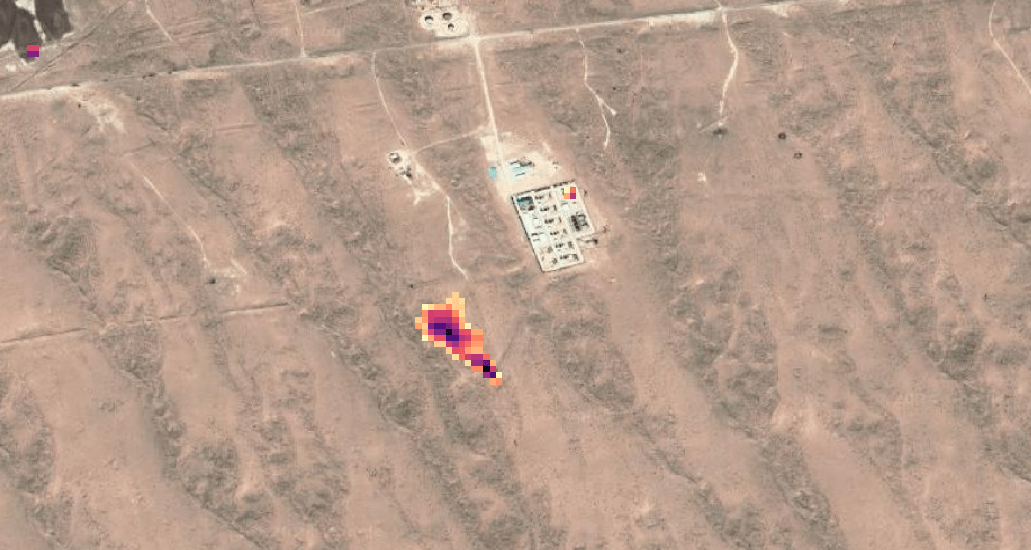
Advancements in satellite technology have significantly enhanced the ability to detect and monitor methane emissions using high resolution satellite data. The main method, called Multi-Band Multi-Pass (MBMP), is an effective technique for detecting methane leaks using Sentinel-2. This approach utilizes imagery from two different days: one day with no emissions and the other with emissions. By comparing the bands of interest (Bands 11 and Band 12) from both days, the method works on their differences to isolate the methane signal. The complexity of the background and the intensity of the emissions determine the clarity of the result; through further processing and cleaning, we can generate a final image that clearly delineates the methane plume. ConclusionMethane emissions are a significant driver of climate change, with immediate and severe impacts on the environment. By leveraging technological advancements and implementing robust policy measures, we can achieve substantial reductions in methane emissions, contributing to a more sustainable and healthier planet. |
- SISTEMA
- July 17, 2024
- 1:02 pm

